|
Россия, Russia, Russian cities, World War II, Moscow, St. Petersburg, Ivan the Terrible, The Great Patriotic War, Palekh, Father Frost, Balalaika, ushanka, Kalashnikov, World War I, Civil War, Russians, Kazakhstan, Ukraine, Belarus, Land, Culture, oil, oil prices, the Internet, money, Peter I, Catherine II, Inflation, Prices, GDP, GDP, food, Putin, Medvedev, Paris, The State, the Slavs, Oprichnina, Stirlitz, Hitler, Blumkin, Tu -160, T-90 T-34, the Russian ruble, the Tsar's Chervonets, Homepage, Stalin, climate weapons | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CONTENTS:
В
какой стране пьют больше всех?
Чему
равен советский рубль в нынешних деньгах
Что Россия экспортирует и
что импортирует
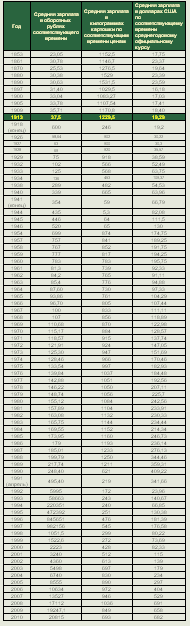
Зарплаты, в Российской
империи, СССР и Российской Федерации
с 1853 по 2010 годы
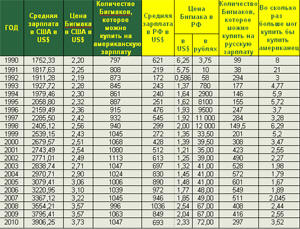
Курс рубля к
доллару и доллара к рублю с 1792 по 2010
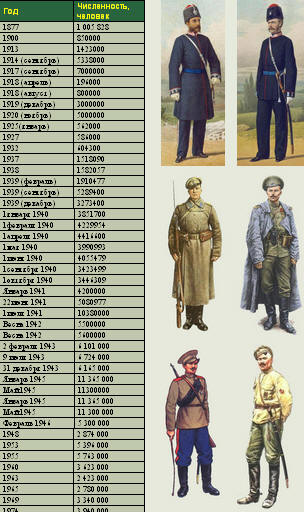
Number of Russian Army personnel since 1877 till present time
|
The total length of roads in Russia is 624,000 sq. kilometers. There are 157,895 localities in Russia, 39,278 (25%) of those are uninhabited.
On the ethnic composition of Russia's population consists almost entirely of the
Russians (79.83%). Minorities include 194 ethnic groups, the most significant of which
are Tatars ? 3.8%, Ukrainians ? 2%, Bashkir ? 1.29%, Chuvash ? 1.12%, the Chechens
? 0.93%, Armenians ? 0.78%, Mordovians ? 0.58%, Avars ? 0.56, Belarusians
? 0.55%, Kazakhs ? 0.45%. However, in the Russian capital Moscow ethnic Great Russians make up only 31% of the population.
Russia ? a federal republic with a bicameral legislature, called the
The two widest separated points in Russia are about 8,000 km (4,971 mi) apart along a geodesic line. These points are: the boundary with Poland on a 60 km (37 mi) long Vistula Spit separating the Gdansk Bay from the Vistula Lagoon; and the farthest southeast of the Kuril Islands. The points which are furthest separated in longitude are 6,600 km (4,101 mi) apart along a geodesic line. These points are: in the west, the same spit; in the east, the Big Diomede Island. The Russian Federation spans 9 time zones. Most of Russia consists of vast stretches of plains that are predominantly steppe to the south and heavily forested to the north, with tundra along the northern coast. Russia possesses 10% of the world's arable land.[109] Mountain ranges are found along the southern borders, such as the Caucasus (containing Mount Elbrus, which at 5,642 m (18,510 ft) is the highest point in both Russia and Europe) and the Altai (containing Mount Belukha, which at the 4,506 m (14,783 ft) is the highest point of Siberia outside of the Russian Far East); and in the eastern parts, such as the Verkhoyansk Range or the volcanoes of Kamchatka Peninsula (containing Klyuchevskaya Sopka, which at the 4,750 m (15,584 ft) is the highest active volcano in Eurasia as well as the highest point of Asian Russia). The Ural Mountains, rich in mineral resources, form a north-south range that divides Europe and Asia. Russia has an extensive coastline of over 37,000 km (22,991 mi) along the Arctic and Pacific Oceans, as well as along the Baltic Sea, Sea of Azov, Black Sea and Caspian Sea. The Barents Sea, White Sea, Kara Sea, Laptev Sea, East Siberian Sea, Chukchi Sea, Bering Sea, Sea of Okhotsk, and the Sea of Japan are linked to Russia via the Arctic and Pacific. Russia's major islands and archipelagos include Novaya Zemlya, the Franz Josef Land, the Severnaya Zemlya, the New Siberian Islands, Wrangel Island, the Kuril Islands, and Sakhalin. The Diomede Islands (one controlled by Russia, the other by the U.S.) are just 3 km (1.9 mi) apart, and Kunashir Island is about 20 km (12.4 mi) from Hokkaido, Japan. Russia has thousands of rivers and inland bodies of water providing it with one of the world's largest surface water resources. The largest and most prominent of Russia's bodies of fresh water is Lake Baikal, the world's deepest, purest, oldest and most capacious freshwater lake.Baikal alone contains over one fifth of the world's fresh surface water. Other major lakes include Ladoga and Onega, two of the largest lakes in Europe. Russia is second only to Brazil in volume of the total renewable water resources. Of the country's 100,000 rivers, the Volga is the most famous, not only because it is the longest river in Europe, but also because of its major role in Russian history. The Siberian rivers Ob, Yenisey, Lena and Amur are among the very longest rivers in the world. The country's original name was Русь (Rus'). This name is originated from the ancient Slavonictribesname of the Rugians, those originally inhabited the island of Rugen (current German name of the island also comes from the name of this tribe), and subsequently settled between the rivers Labe (Elbe) and the Odra (Oder). The tribe is first mentioned by the Roman author of the I century Publius Cornelius Tacitus in his book "De origine et situ Germanorum", written in 1998 AD. In ancient times, the sounds [g] and [z] were alternants in the Slavic languages. Thus, the plural of the word "RUG" sounded like "Ruzi. In the Novgorod dialect occurred reduction of sound [z] to [s]. Thus the word Rugs came to the word "Rus'". The word "Russia" comes from the word "?????" ? the Greek name of Russia in the Byzantine sources.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Climate data for Russia | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) |
21.2 (70.2) |
23.8 (74.8) |
30.3 (86.5) |
34.0 (93.2) |
37.7 (99.9) |
43.2 (109.8) |
45.4 (113.7) |
43.5 (110.3) |
41.5 (106.7) |
33.7 (92.7) |
29.1 (84.4) |
25.0 (77) |
45.4 (113.7) |
| Record low °C (°F) |
?71.2 (-96.2) |
?64.4 (-83.9) |
?60.6 (-77.1) |
?46.4 (-51.5) |
?28.9 (-20) |
?9.7 (14.5) |
?9.3 (15.3) |
?17.1 (1.2) |
?25.3 (-13.5) |
?47.6 (-53.7) |
?58.5 (-73.3) |
?62.8 (-81) |
?71.2 (-96.2) |

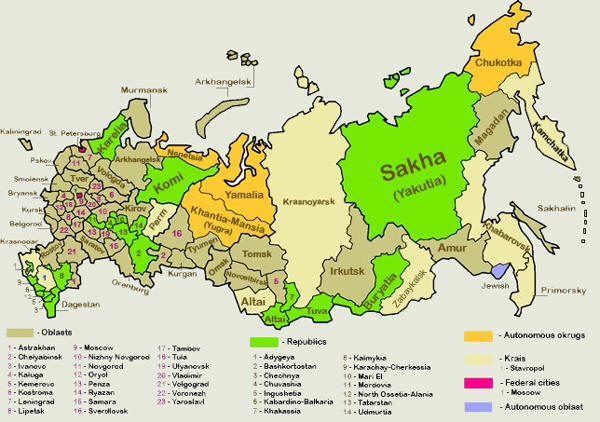
The Russian Federation comprises 83 federal subjectsThese subjects have equal representation—two delegates each—in the Federation Council. However, they differ in the degree of autonomy they enjoy.
46 oblasts (provinces): most common type of federal subjects, with federally appointed governor and locally elected legislature.
21 republics: nominally autonomous; each has its own constitution, president, and parliament. Republics are allowed to establish their own official language alongside Russian but are represented by the federal government in international affairs. Republics are meant to be home to specific ethnic minorities.
9 krais (territories): essentially the same as oblasts. The "territory" designation is historic, originally given to frontier regions and later also to administrative divisions that comprised autonomous okrugs or autonomous oblasts.
4 autonomous okrugs (autonomous districts): originally autonomous entities within oblasts and krais created for ethnic minorities, their status was elevated to that of federal subjects in the 1990s. With the exception of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, all autonomous okrugs are still administratively subordinated to a krai or an oblast of which they are a part.
1 autonomous oblast (the Jewish Autonomous Oblast): originally autonomous oblasts were administrative units subordinated to krais. In 1990, all of them except the Jewish AO were elevated in status to that of a republic.
2 federal cities (Moscow and St. Petersburg): major cities that function as separate regions.
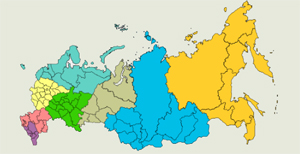
Federal subjects are grouped into 8 federal districts, each administered by an envoy appointed by the President of Russia.[110] Unlike the federal subjects, the federal districts are not a subnational level of government, but are a level of administration of the federal government. Federal districts' envoys serve as liaisons between the federal subjects and the federal government and are primarily responsible for overseeing the compliance of the federal subjects with the federal laws.













 Russia
established worldwide power and influence from the times of the Russian
Empire to being the largest and leading constituent of the Soviet Union,
the world's first constitutionally socialist state and a recognized
superpower, that played a decisive role in the Allied victory in World
War II. The Soviet era saw some of the greatest technology achievements
of the 20th century, such as the world's first human spaceflight. The
Russian Federation was founded following the dissolution of the Soviet
Union in 1991.
Russia
established worldwide power and influence from the times of the Russian
Empire to being the largest and leading constituent of the Soviet Union,
the world's first constitutionally socialist state and a recognized
superpower, that played a decisive role in the Allied victory in World
War II. The Soviet era saw some of the greatest technology achievements
of the 20th century, such as the world's first human spaceflight. The
Russian Federation was founded following the dissolution of the Soviet
Union in 1991.